What are sheet metal components and why are they so important to various industries?
 2025.05.16
2025.05.16
 Industry News
Industry News
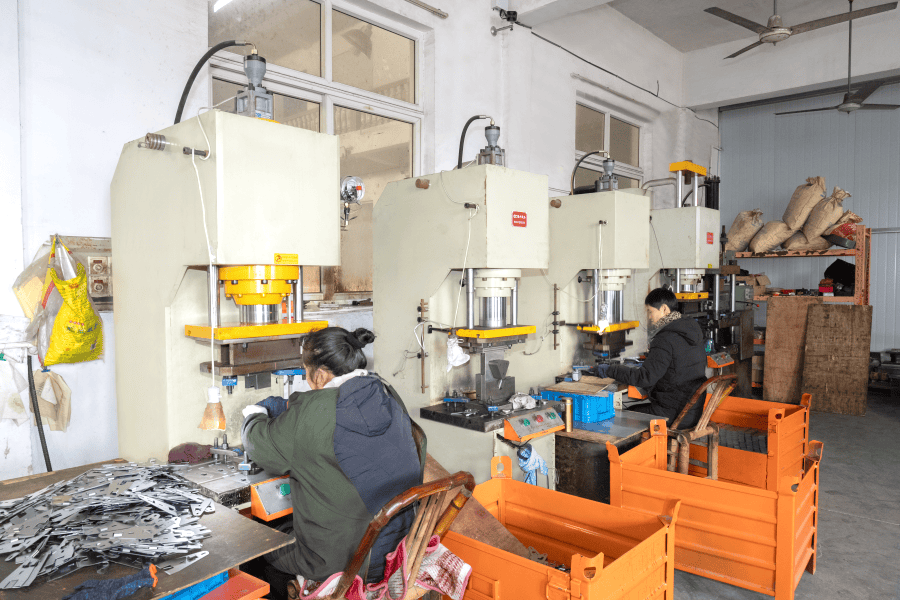
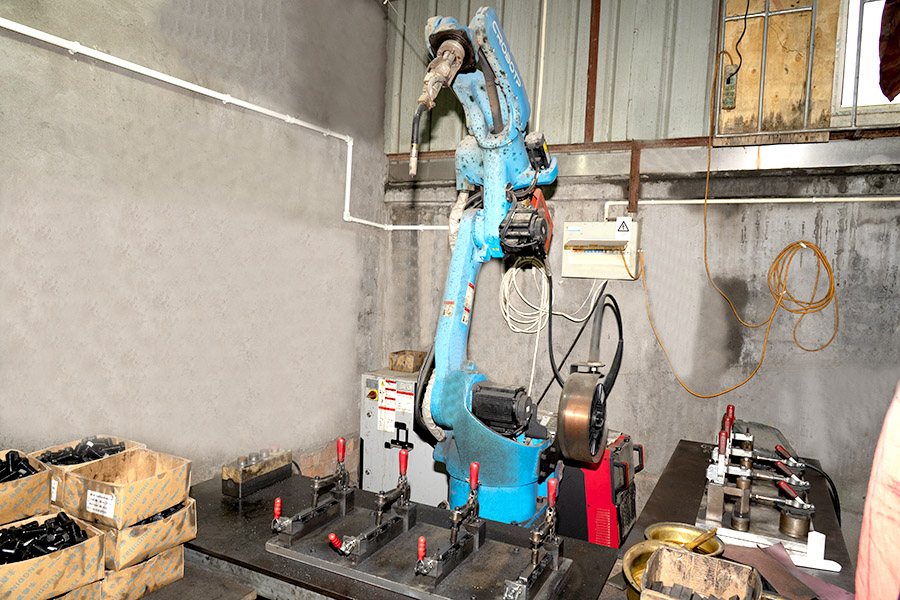
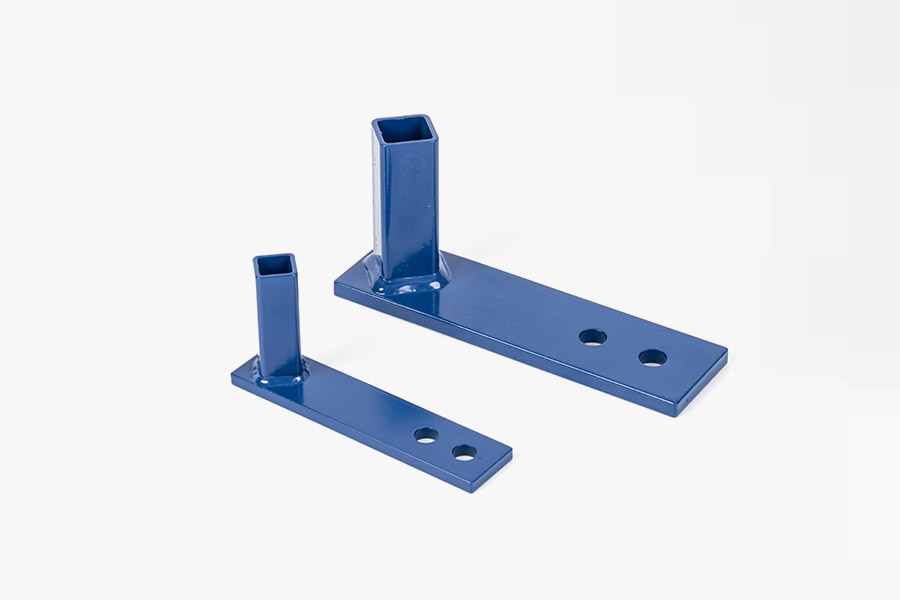
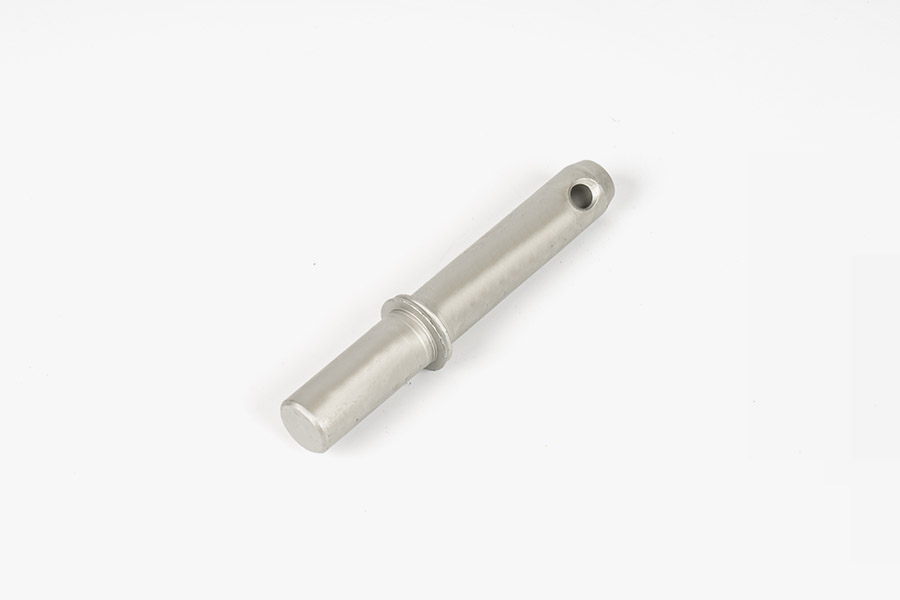
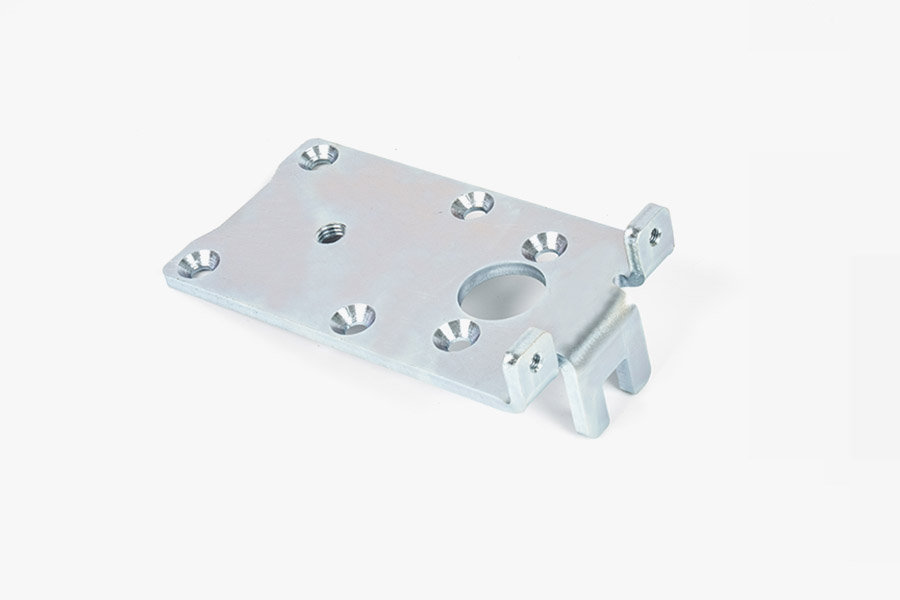
Sheet metal parts are products made by processing metal sheets into various shapes and sizes. The core technologies involved in sheet metal manufacturing processes include precision cutting, bending, stamping, stretching, welding, etc., which are widely used in many industries such as automobiles, aerospace, electronics, and construction. Through these processes, metal sheets can be processed into various parts with complex structures and unique shapes. The production of sheet metal parts starts with the cutting process. Common cutting methods include laser cutting, water jet cutting, and plasma cutting. These methods can efficiently and accurately cut metal sheets into the required shape. The cut metal sheets will be sent to the bending equipment for bending operations. The bending process can convert flat metal into three-dimensional forms with angles or curves to meet specific design requirements. In this process, the accuracy of the size, angle, and shape of the sheet metal parts is key. With the continuous advancement of technology, sheet metal manufacturing has now introduced more automated equipment, which has greatly improved the accuracy and efficiency of the manufacturing process.
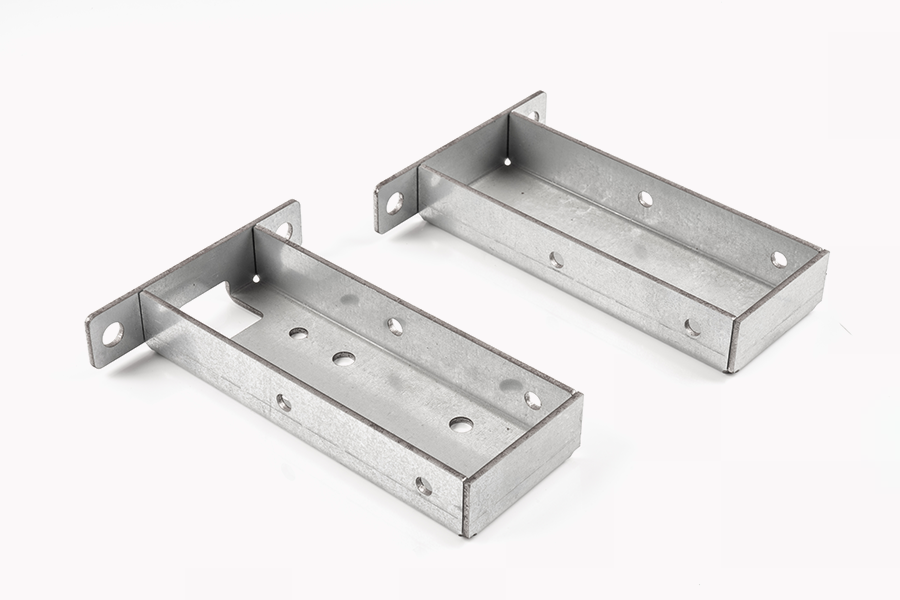
Sheet metal parts are usually used to manufacture parts that are strong, durable, and easy to process. Their applications are very wide, covering almost all industrial fields. For example, in the automotive industry, sheet metal parts are widely used in the manufacture of parts such as car bodies, chassis, doors, and hoods. As the requirements for lightweight and safety of automobiles continue to increase, sheet metal manufacturing has become an important process to meet these requirements. Sheet metal parts can not only provide good structural support, but also achieve a balance between lightness and high strength through optimized design. Especially in the design of the body shell, sheet metal manufacturing technology helps automakers reduce the weight of the body and improve safety through reasonable structural design and material selection.
In the field of aerospace, sheet metal parts also play an irreplaceable role. The outer shell and internal structure of the aircraft often use sheet metal parts, which need to be lightweight, strong and corrosion-resistant. In this demanding environment, sheet metal manufacturing not only needs to ensure precise size and shape, but also the quality and safety of each component. Through precise sheet metal processing technology, aircraft can withstand huge aerodynamic pressure and environmental changes during flight while ensuring structural integrity and safety.
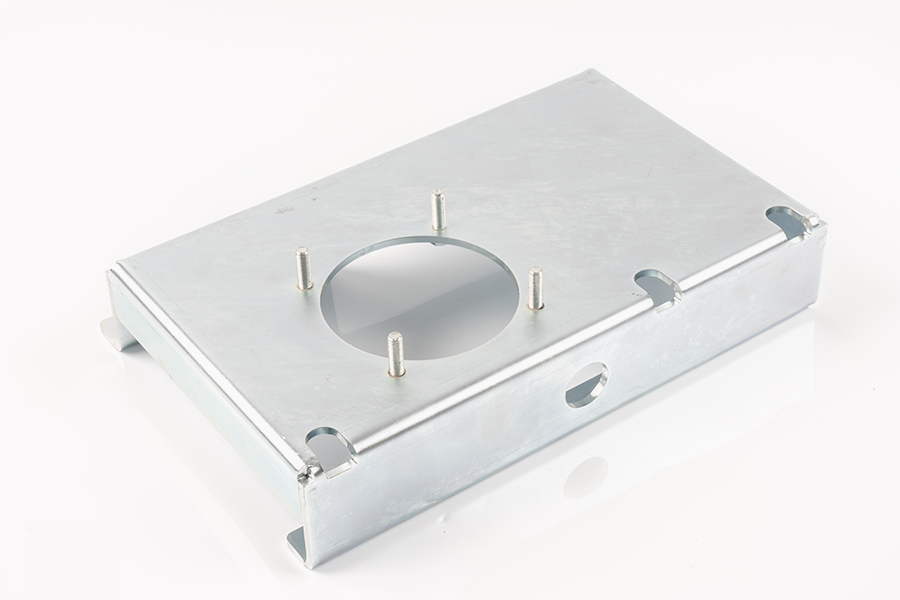
In the manufacture of electronic products, sheet metal parts are widely used in the production of various shells. For example, the production of electronic equipment shells such as computer cases and mobile phone shells mostly relies on sheet metal processes. These shells not only need to protect the internal components, but also need to have good heat dissipation performance, shock resistance and aesthetics. Sheet metal processing can achieve complex designs through precision cutting, stamping and bending technologies to ensure the quality and functionality of these products.
The construction industry also has a great demand for sheet metal parts, and sheet metal materials are widely used in the manufacture of building components such as roofs, exterior walls, door and window frames. Sheet metal parts not only provide stable structural support, but also improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics through different surface treatments. The durability of sheet metal parts makes them one of the important materials in the construction industry, and they can maintain a long service life under harsh climatic conditions.
One of the biggest advantages of sheet metal manufacturing technology is its precision and diversity. Through technologies such as laser cutting and water jet cutting, sheet metal manufacturing can achieve very precise sizes and shapes. Even with very complex geometric shapes, sheet metal processing can produce highly consistent and accurate parts. This allows sheet metal parts to meet the high precision requirements of different fields. For example, in industries such as electronics and medical equipment that require extremely high dimensional accuracy, the precision processing of sheet metal parts is particularly important.
Sheet metal parts can also be functionally designed according to different application requirements. For example, in the automotive industry, sheet metal parts need to have not only strength and rigidity, but also certain elasticity and impact resistance. Through precise design and control, sheet metal processes can ensure that products meet strength requirements while avoiding unnecessary material waste, thereby achieving lightweight design. In the aerospace field, sheet metal parts often need to have stronger corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, which requires fine adjustme nts in material selection and surface treatment.
The cost-effectiveness of sheet metal parts is also one of the important reasons for their widespread application. With the development of automation technology, the production efficiency of sheet metal manufacturing has been greatly improved. Through automated equipment and precision tools, the labor cost and time consumption in the production process have been effectively reduced. Especially in large-scale production, the cost advantage of sheet metal parts is more obvious, making this process a widely used manufacturing method in many industries.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体