What Makes Stamping Metal Parts Essential for Modern Manufacturing and Industry Applications?
 2026.01.15
2026.01.15
 Industry News
Industry News
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing world, precision and efficiency are the cornerstone of success. The demand for reliable, cost-effective, and durable components has never been higher. Stamping Metal Parts are becoming increasingly integral in this context. These parts are produced using a technique known as metal stamping, where metal sheets are shaped and cut into specific designs under extreme pressure. As industries continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, the role of stamping metal parts has expanded to virtually every sector, from automotive to electronics, aerospace, and beyond.
This article delves into the significance of stamping metal parts in modern manufacturing, examining their production process, applications, advantages, and the emerging technologies that make them indispensable in a variety of industries.
What Are Stamping Metal Parts?
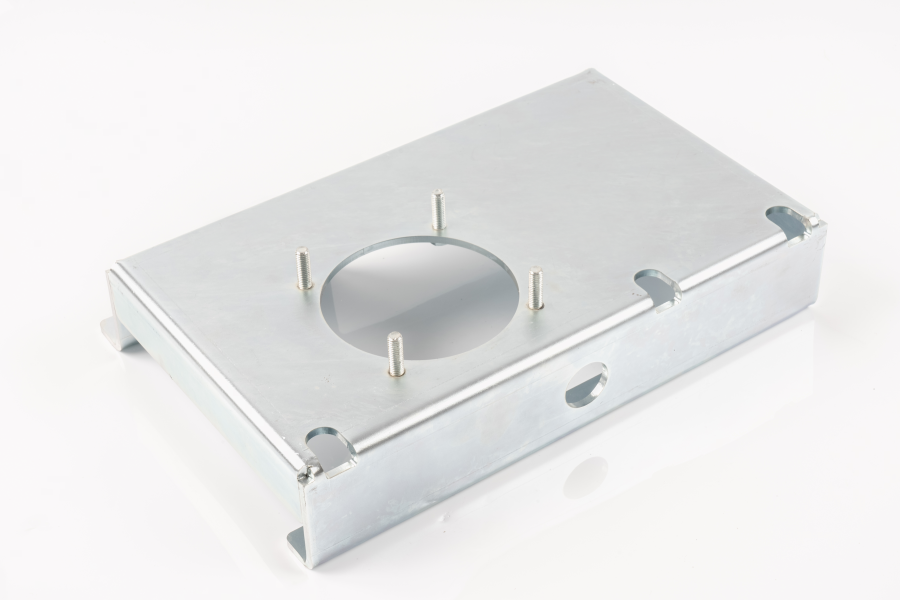
Stamping metal parts refer to components that are made from sheet metal using a stamping press. The press utilizes tools such as dies and molds to cut, shape, and form the metal into the desired specifications. These parts can be found in a wide range of applications, from simple brackets to complex automotive components. They are used extensively because of their precision, durability, and relatively low cost of production.
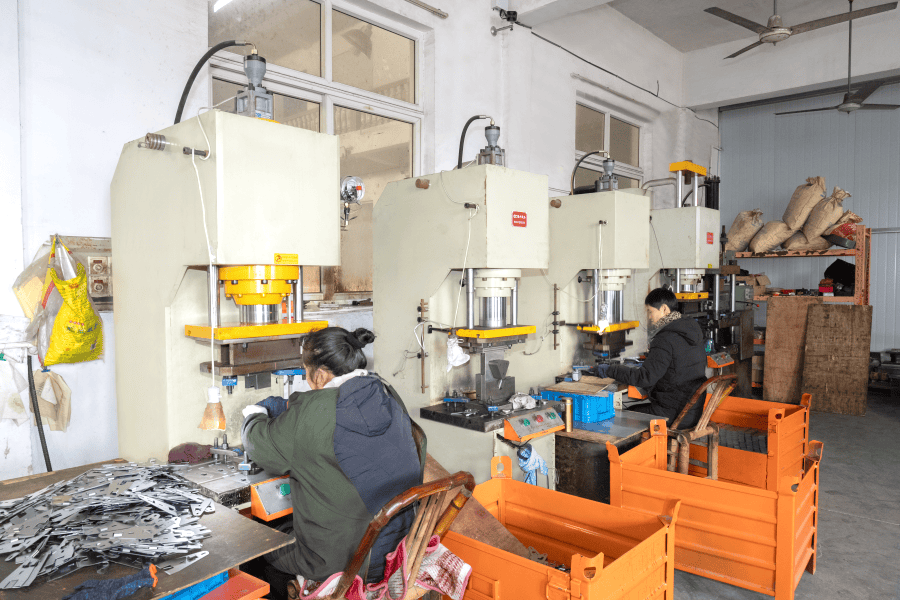
The process of metal stamping involves several steps, including cutting, punching, bending, and coining. The metal sheets are first fed into the press, where they are then subjected to various die operations that form them into the required shape. The process is highly automated, making it suitable for mass production.
The Advantages of Stamping Metal Parts
There are several reasons why stamping metal parts have become so popular across different industries. Below are the key advantages that this manufacturing process offers:
1. High Precision and Consistency
One of the standout features of stamping metal parts is their ability to maintain high precision and consistency. Once a die is created for a specific part, it can produce thousands or even millions of parts with very little variation in size and shape. This makes stamping an ideal choice for industries that require exact tolerances and repeatability.
2. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Metal stamping is incredibly cost-efficient, especially for high-volume production. While the initial setup costs for tooling and dies can be high, once set up, the cost per part dramatically decreases. This makes it perfect for applications where large quantities of parts are required. The ability to produce large volumes with minimal labor also contributes to the reduced overall production cost.
3. Versatility in Design
Stamping metal parts can be produced in virtually any shape and size, offering incredible versatility. Whether it’s a simple flat piece, a complex shape, or a multi-step process involving bending, forming, and punching, the stamping process can create a wide variety of metal parts. Furthermore, multiple processes can be integrated into one tool, making it easy to customize parts as needed.
4. Durability and Strength
The nature of the metal used in stamping, combined with the high pressures applied during the process, results in parts that are not only lightweight but also strong and durable. For instance, steel and aluminum, two common materials used in metal stamping, offer excellent tensile strength, making them suitable for use in high-stress environments such as automotive frames and aerospace components.
5. Efficiency in Mass Production
Because metal stamping is highly automated, the process is extremely fast. This high throughput capability allows manufacturers to produce large quantities of parts in a short period, enhancing the efficiency of production cycles and reducing lead times. This is a critical advantage in industries where time-to-market is crucial, such as the automotive and electronics sectors.
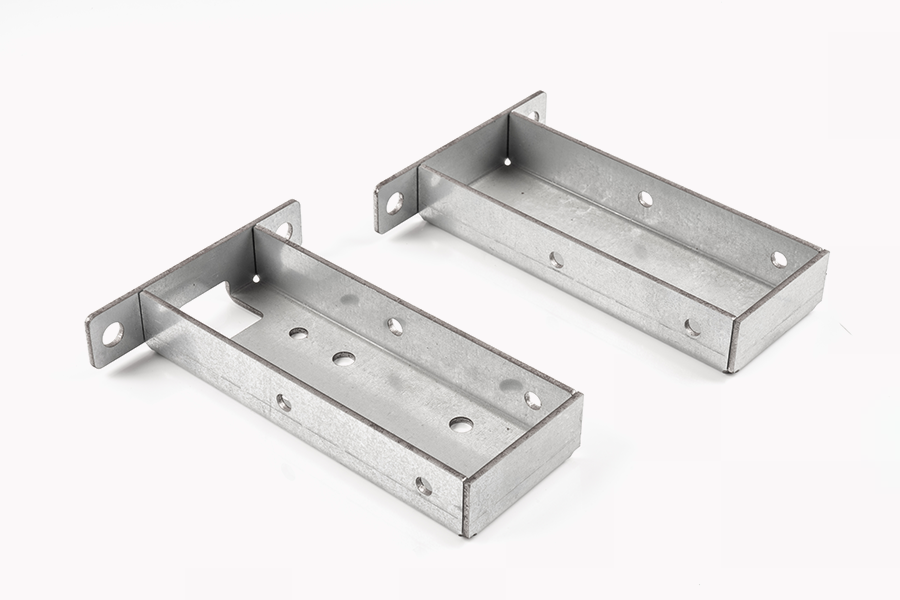
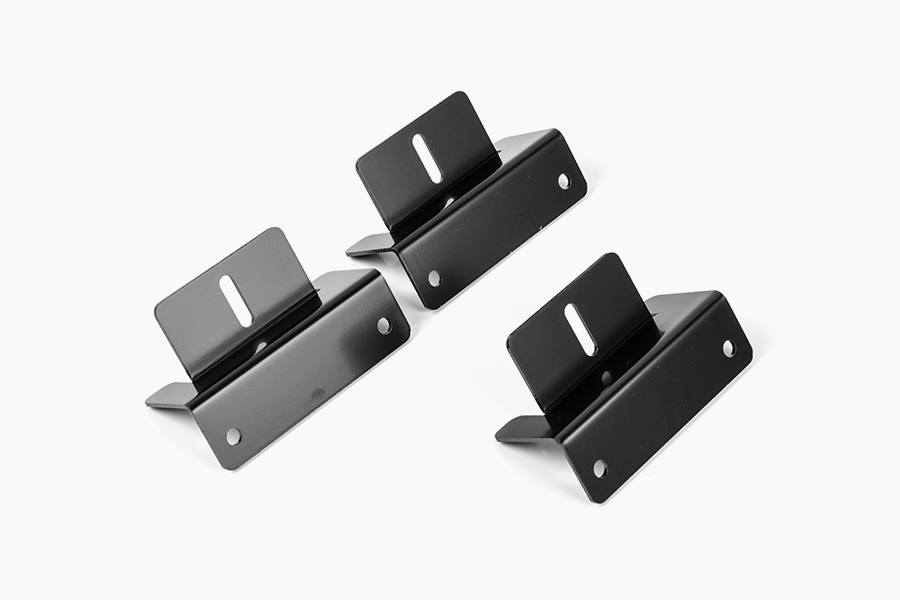
Applications of Stamping Metal Parts
The versatility of stamping metal parts means that they have a wide range of applications across various industries. Let’s look at some of the primary sectors where stamped metal components are integral:
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is one of the largest consumers of stamped metal parts. These parts are used in the manufacturing of everything from body panels and chassis components to engine parts and suspension systems. The ability to produce large quantities of automotive parts that meet strict safety and quality standards has made metal stamping essential for the automotive sector.
Components like car body panels, brackets, and exhaust parts are just a few examples of stamped metal parts in vehicles. Metal stamping allows for the mass production of these components at a relatively low cost, making vehicles more affordable for consumers while maintaining structural integrity.
2. Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, stamped metal parts are used in the production of various components such as connectors, housings, and brackets. As electronic devices continue to shrink in size and become more complex, the demand for precision-stamped metal parts that can handle tight tolerances and miniaturization increases. These parts are essential for ensuring the stability, durability, and functionality of electronic devices like smartphones, computers, and appliances.
3. Aerospace and Aviation
Aerospace and aviation are two sectors where performance and safety are paramount. Stamped metal parts are often used in critical systems, such as aircraft frames, turbine engine components, and landing gear assemblies. The strength-to-weight ratio of stamped metal parts makes them ideal for these applications, where minimizing weight while maintaining structural integrity is essential.
The aerospace industry often uses titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum for metal stamping, which can withstand extreme environmental conditions, including high pressures and temperatures.
4. Consumer Goods
Consumer goods manufacturers also rely heavily on stamping metal parts for everything from kitchen appliances to furniture. Components such as handles, hinges, and internal mechanisms in items like refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines are commonly produced using metal stamping techniques. This ensures that the parts are both strong and cost-effective for mass production.
5. Industrial Equipment and Machinery
Many industrial applications, including heavy machinery, utilize stamped metal parts for both structural and functional components. These parts are critical for manufacturing equipment used in construction, mining, and agricultural industries. Stamped parts are used for everything from engine blocks and frames to valves and gears, where their strength, durability, and precision are indispensable.
Innovations and Trends in Stamping Metal Parts
As industries evolve, so does the technology behind stamping metal parts. New innovations are constantly improving the efficiency, precision, and versatility of the metal stamping process. Some of the current trends include:
1. Advanced Tooling and Dies
Advancements in tooling technology are making metal stamping more precise and capable of producing more intricate designs. For example, computer-aided design (CAD) software allows engineers to design complex geometries that were previously difficult to manufacture. High-tech dies are being created using rapid prototyping, reducing lead times and improving part accuracy.
2. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in manufacturing processes, and metal stamping is no exception. Companies are now using more eco-friendly materials, recycling scrap metal, and implementing energy-efficient practices to reduce the environmental impact of the stamping process.
3. Hybrid Stamping Technologies
Some manufacturers are combining traditional metal stamping with newer technologies like additive manufacturing (3D printing). Hybrid stamping allows for more complex parts to be made with greater speed and fewer resources, offering both customization and mass production capabilities.
Technical Specifications of Stamping Metal Parts
Here’s an overview of the typical technical specifications and operational parameters associated with stamping metal parts:
| Feature | Specification | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Brass | Versatility across industries |
| Precision | ±0.1 mm | High accuracy in production |
| Tolerance | Tight tolerance (±0.02 mm) | Ensures consistent part quality |
| Process Type | Progressive, Single Hit, Deep Drawing | Adaptability to different designs |
| Weight Capacity | Up to several tons per press | Handles large-scale production |
| Automation | Fully automated production | Increases throughput and efficiency |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, Electronics, Aerospace, Consumer Goods | Wide application range |
Why Choose Stamping Metal Parts for Your Manufacturing Needs?
As industries continue to demand greater efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness, stamping metal parts are positioned as a fundamental solution for achieving these goals. The ability to produce large quantities of high-quality, durable parts at a lower cost, combined with their versatility and precision, makes metal stamping indispensable in modern manufacturing.
From the automotive and electronics industries to aerospace and industrial machinery, stamped metal parts are key to keeping production lines running smoothly, while simultaneously helping companies maintain competitive pricing. With continued advancements in stamping technology and material science, the role of stamping metal parts will only grow more significant as the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve.
By choosing stamping metal parts for your production needs, you’re ensuring that you remain at the forefront of technological innovation while maximizing both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The future of manufacturing lies in precision, automation, and versatility—qualities that stamping metal parts deliver in abundance.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体