Are high-precision stampings surface treated for corrosion resistance or surface finish?
 2025.05.16
2025.05.16
 Industry News
Industry News
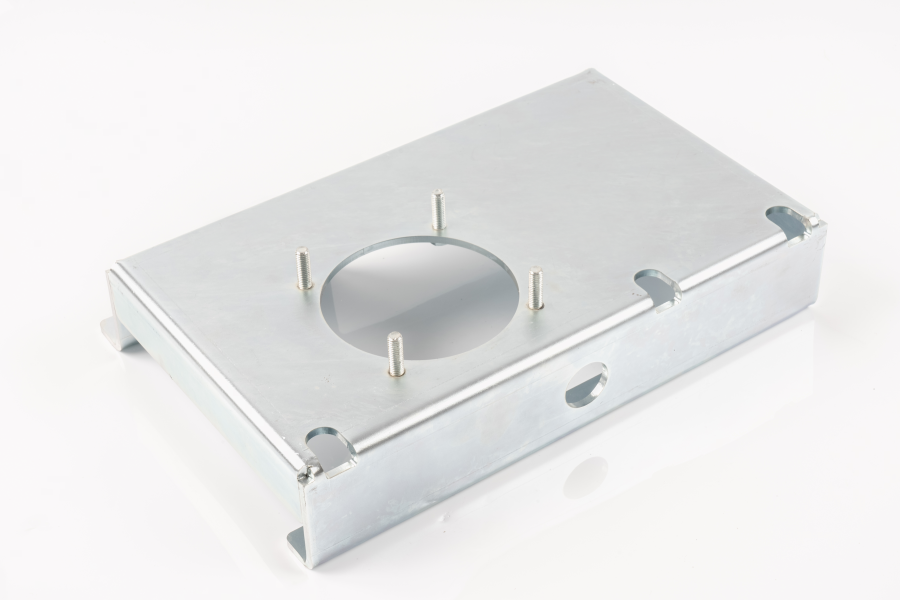
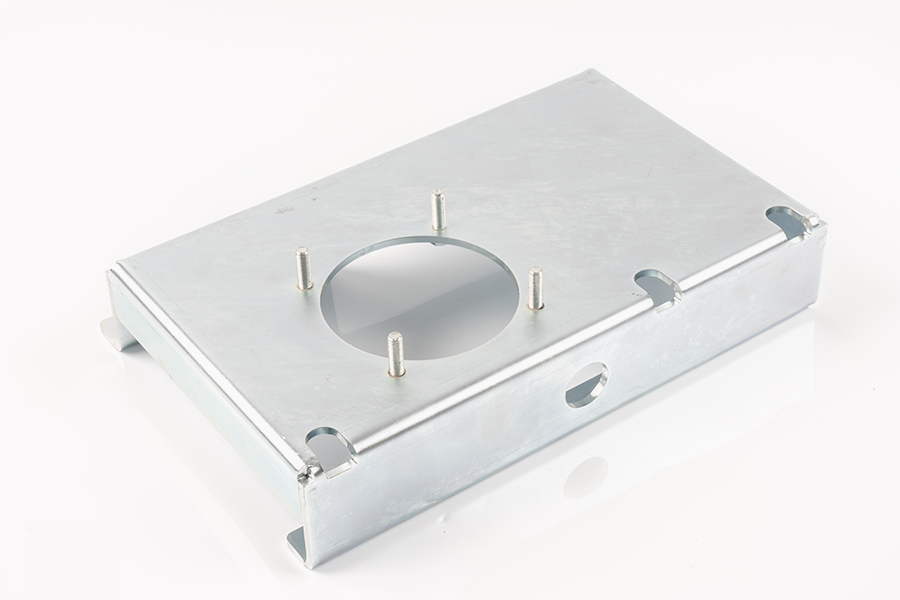
In the manufacturing process of high-precision stamping parts, in addition to high standards for dimensional accuracy and structural shape, surface treatment also occupies an important position that cannot be ignored. Surface treatment is not only related to the appearance quality of parts, but also directly affects their corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and surface finish, thereby improving the stability and ductility of parts in various complex environments.
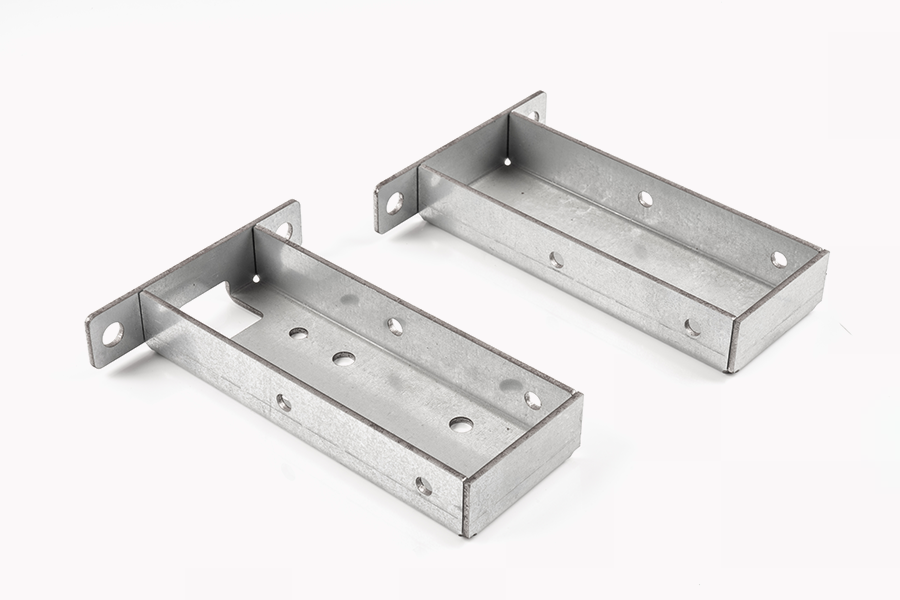
Stamping parts themselves are often used in machinery, automobiles, electronics, aviation and other fields. In actual application, they are often exposed to moisture, salt spray, acid, alkali or high temperature environments. If the surface is not treated, it is easy to affect the function or even cause failure due to oxidation, rust or impurity deposition. Therefore, companies usually choose appropriate surface treatment processes to enhance their performance according to the product application environment and customer needs.
Common surface treatment methods include electroplating, spraying, oxidation, passivation, phosphating and mechanical polishing. Among them, electroplating process is widely used in high-precision stamping parts. It can form a metal film on the surface of the substrate to isolate air and moisture. There are rich types of coatings, such as zinc plating, nickel plating, chrome plating, etc., which can be flexibly selected according to actual use needs. Electroplating not only enhances corrosion resistance, but also improves conductivity or welding performance, which is suitable for precision parts with electrical performance requirements.
Another common method is spraying or dipping, which covers the surface with a layer of resin or paint film to make the parts have better protection against external impact, friction and chemical corrosion. This method is usually suitable for occasions with specific requirements for color, aesthetics and adhesion. Especially in the automotive field, some exposed parts need to meet the requirements of appearance consistency while ensuring dimensional accuracy, and the spraying process can provide additional support.
For application environments with higher requirements for corrosion resistance, oxidation and passivation treatment are frequently used. In particular, for stainless steel stampings, after passivation treatment, a dense protective film layer can be formed on its surface, which can increase the resistance to corrosive media such as acids and alkalis without changing the basic dimensions. Oxidation treatment is often used for aluminum stampings, which can not only improve hardness but also extend service life.
In addition to chemical and electrochemical methods, mechanical methods such as polishing, wire drawing, sandblasting, etc. also play an important role. Polishing can improve the flatness of the surface of parts, reduce tiny burrs and stamping marks, and thus reduce friction and wear during subsequent assembly. The wire drawing process gives the surface a special texture, which helps to improve the appearance and texture of the product and is widely used in decorative precision parts. Sandblasting is mostly used to clean oxide scale and improve adhesion, providing a more stable foundation for subsequent coatings.
Surface treatment is not only reflected in functional improvement, but also combined with the concept of green manufacturing. Nowadays, more and more companies are introducing environmentally friendly materials and processes in the surface treatment process, striving to reduce the impact on the environment while meeting the performance. For example, lead-free plating and low-VOC spray materials have gradually become a trend, reflecting the focus on sustainable development in the manufacturing process.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体