Stamping Metal Parts vs. Sheet Metal Parts: A Comprehensive Comparison
 2025.09.10
2025.09.10
 Industry News
Industry News
In the world of manufacturing, precision, strength, and durability are essential when producing parts for a wide variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and more. Stamping Metal Parts and Sheet Metal Parts are two common options, each offering distinct advantages and uses depending on the specific needs of a project. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different manufacturing processes, materials, and end applications.
What Are Stamping Metal Parts?
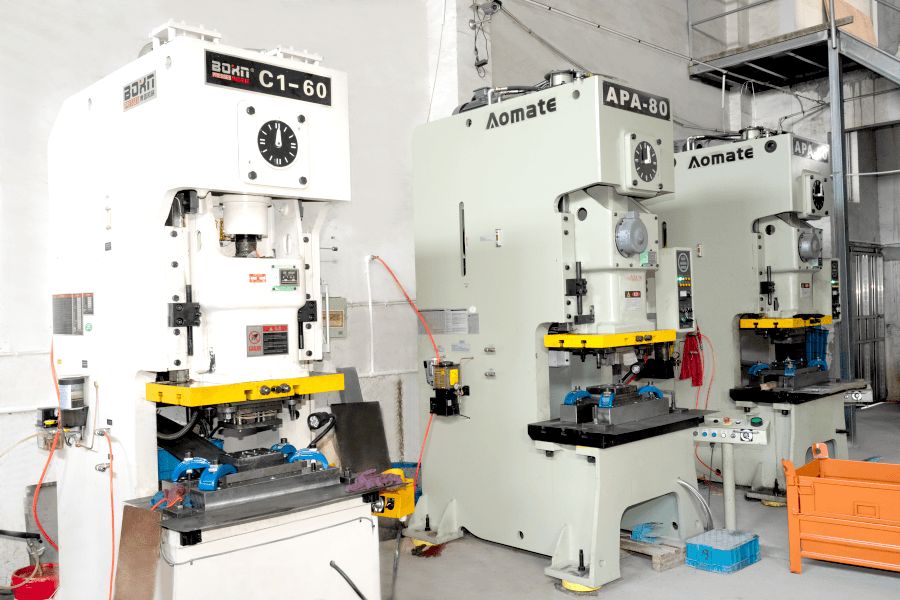
Stamping Metal Parts refers to a process where a metal sheet (usually cold-rolled steel, aluminum, or brass) is placed into a press and shaped or cut using a die. The stamping process involves applying high pressure to the sheet to create parts in the desired shape and size, often used for components that require high precision and durability.
Common processes involved in stamping include blanking, piercing, embossing, bending, and drawing. These processes enable manufacturers to produce parts with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and consistent quality, making them ideal for applications like automotive components, electronics, and appliances.

What Are Sheet Metal Parts?
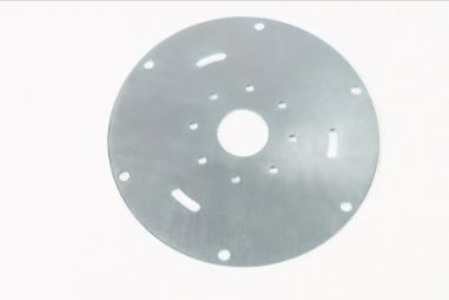
Sheet Metal Parts is a broader term that encompasses any metal component made by cutting, bending, or forming thin sheets of metal. While Stamping Metal Parts is one method for producing Sheet Metal Parts, there are other processes like laser cutting, water jet cutting, rolling, and hydraulic press forming used to shape the metal sheets.
Sheet Metal Parts are widely used in industries such as construction, HVAC, and manufacturing. These parts can be made from a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and titanium, offering a diverse range of properties and applications.
Key Differences Between Stamping Metal Parts and Sheet Metal Parts
| Feature | Stamping Metal Parts | Sheet Metal Parts |
| Manufacturing Process | Uses a die to press metal sheets into shape with high pressure | Includes various processes such as cutting, bending, and rolling |
| Material | Typically uses cold-rolled steel, aluminum, or brass | Can use a variety of metals, including aluminum, steel, copper, etc. |
| Precision and Tolerance | High precision and tight tolerances, ideal for complex designs | Tolerances may vary depending on the process used |
| Strength | Offers high strength and durability due to the nature of stamping | Strength varies depending on the material and forming process |
| Applications | Common in automotive, electronics, and appliances | Widely used in HVAC, construction, enclosures, and other industries |
| Cost | Typically more cost-effective for high-volume production | Cost can vary greatly depending on the material and process used |
| Production Speed | Fast production time for high-volume runs | Production speed can vary depending on the complexity and process |
Advantages of Stamping Metal Parts
-
High Precision and Consistency: Stamping allows for the production of parts with tight tolerances and complex shapes, which are essential for industries that require high precision, such as the automotive and electronics sectors.
-
Cost-Effective for High Volumes: Once the die is created, stamping is highly cost-efficient for large-volume production. The process can produce hundreds or thousands of parts per hour, making it ideal for mass production environments.
-
Durability: Stamping Metal Parts are known for their strength and durability. The high pressure used during the stamping process results in parts that are able to withstand heavy loads and wear, making them suitable for demanding applications.
-
Versatility in Design: Stamping can create parts with complex shapes and features, including holes, curves, and embossments. This makes it a versatile option for industries requiring intricate and varied designs.
Disadvantages of Stamping Metal Parts
-
Initial Tooling Costs: The upfront cost of designing and manufacturing stamping dies can be high. This makes stamping less cost-effective for low-volume production runs.
-
Limited Material Flexibility: While stamping is effective for certain metals like steel and aluminum, it is not suitable for all materials, particularly very hard or brittle metals.
-
Limited Thickness Range: Stamping is typically best suited for thin to medium-thickness materials. For very thick sheets, other processes might be more appropriate.
Advantages of Sheet Metal Parts
-
Material Flexibility: Sheet Metal Parts can be made from a wide range of materials, such as aluminum, stainless steel, brass, titanium, and more, offering greater material choices for different properties like corrosion resistance, strength, and weight.
-
Wide Range of Applications: Sheet Metal Parts are extremely versatile and can be used in industries ranging from construction (such as roofing and wall panels) to HVAC (such as ducts and vents) and even electronics (such as enclosures and chassis).
-
Lower Setup Costs for Low Volume: Unlike stamping, which requires significant die costs, sheet metal fabrication processes like laser cutting or water jet cutting are less expensive for small to medium production runs. This makes it an attractive option for companies that don’t require large quantities of parts.
-
Ease of Modification: The processes used for making Sheet Metal Parts, like laser cutting or bending, are flexible and allow for easy modifications or adjustments to designs, which is beneficial for prototyping or custom projects.
Disadvantages of Sheet Metal Parts
-
Lower Precision for Complex Shapes: While Sheet Metal Parts can be formed with many processes, they may not achieve the same level of precision as Stamping Metal Parts for intricate or highly complex geometries, especially when high volumes are required.
-
Potential for Higher Labor Costs: Some sheet metal processes, such as manual bending, can require significant labor, which increases the overall production costs.
-
Less Suitable for Mass Production: In comparison to stamping, sheet metal fabrication can be slower and less cost-effective for large-scale production runs.
Both Stamping Metal Parts and Sheet Metal Parts have their distinct advantages and are suited to different manufacturing needs. Stamping Metal Parts is the preferred method for producing high-precision, durable parts in large volumes, making it ideal for industries like automotive, electronics, and appliance manufacturing. However, the high initial tooling costs make it less viable for low-volume production runs.
On the other hand, Sheet Metal Parts offers greater flexibility in terms of material selection, process options, and applications, especially for construction, HVAC, and custom fabrication projects. The ability to use different forming techniques like laser cutting or water jet cutting also makes Sheet Metal Parts an excellent choice for prototyping and low-to-medium volume runs.
When selecting between these two options, it is essential to consider factors like the required precision, production volume, material requirements, and cost constraints. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both methods, you can ensure the right choice for your manufacturing needs.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体