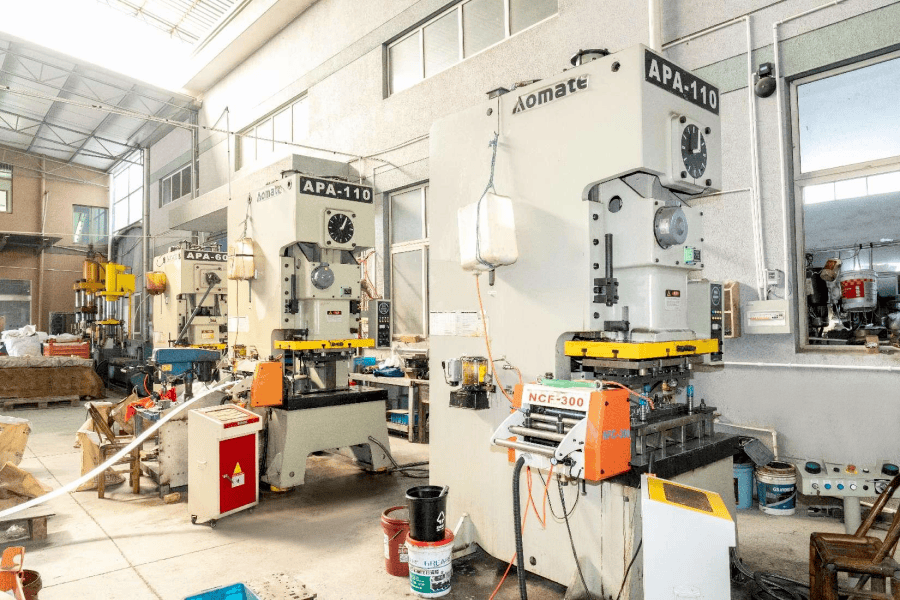
What Are Welding Parts and How Do They Ensure Strength and Reliability in Manufacturing?
 2025.09.25
2025.09.25
 Industry News
Industry News
What Are Welding Parts in Industrial Production?
Definition of Welding Parts
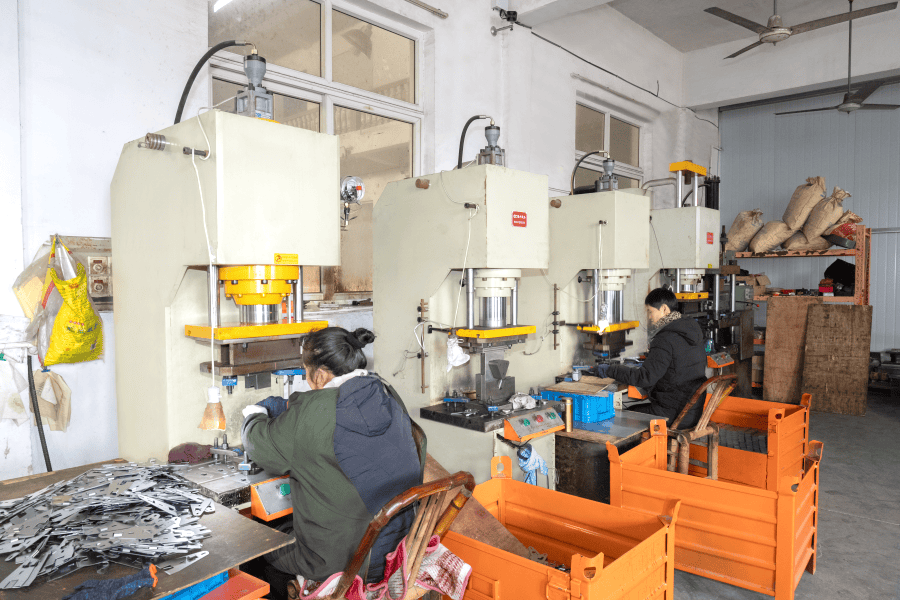
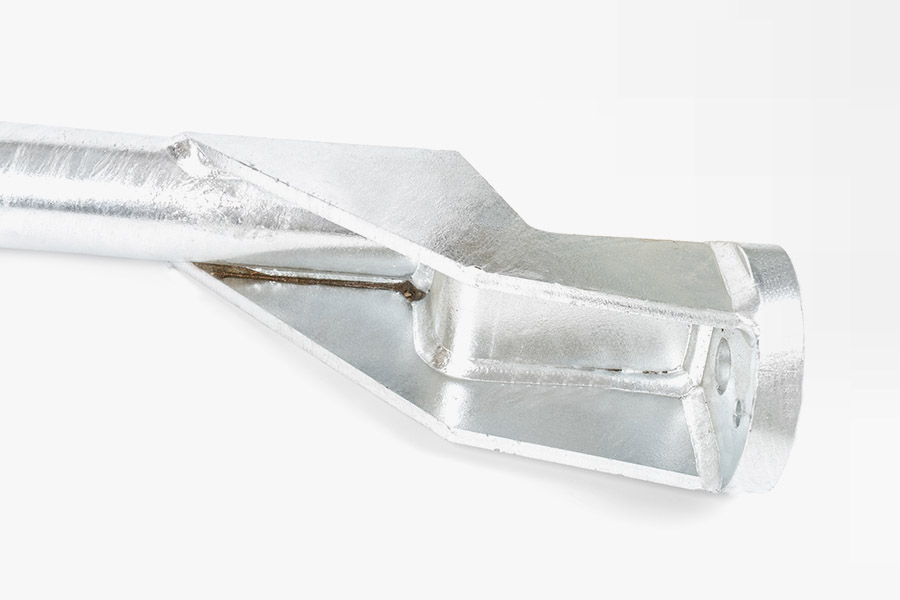
Welding parts refer to components that are created or assembled by the process of welding, which involves joining materials—typically metals or thermoplastics—using high heat to melt the parts and allow them to fuse together. In industrial production, welding is commonly used for manufacturing and assembling structural components, machinery parts, and other critical components that require strong, durable connections. Welding parts are essential in industries such as automotive, construction, aerospace, and heavy machinery, where robust and reliable connections are crucial.
Difference Between Welded Parts and Machined Parts
The primary difference between welding parts and machined parts lies in the production process and the type of materials they are made from:
Welded Parts: These parts are created by joining two or more pieces of material together using welding techniques, such as arc welding, MIG welding, or TIG welding. The process involves applying heat to the materials until they melt and fuse, creating a strong bond. Welded parts are commonly used for large, heavy, or complex structures where other methods, like machining, may not be feasible.
Machined Parts: Machined parts are created by removing material from a solid block or billet of metal using cutting, grinding, or drilling tools. This is a subtractive manufacturing process that results in precise, highly accurate components. Machined parts are often used in industries that require high precision and detailed specifications, such as aerospace or automotive engineering.
While welding parts are often used for their ability to join large, bulky materials, machined parts are preferred when fine tolerances and smooth surfaces are required. Both processes have their advantages, and the choice between welding and machining depends on the specific requirements of the project, including material properties, part complexity, and cost-efficiency.
Why Welding is Widely Used in Heavy-Duty Industries?
Welding is widely used in heavy-duty industries for several reasons, making it a vital process in sectors like construction, automotive manufacturing, shipbuilding, and mining. The key advantages include:
Strength and Durability: Welding parts create strong, permanent joints that are highly durable and capable of withstanding significant stresses and environmental factors. This makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications where the integrity of the structure is crucial, such as in bridges, cranes, and heavy machinery.
Flexibility in Material Use: Welding can be used to join a wide variety of metals and alloys, such as steel, aluminum, and titanium. This versatility allows manufacturers to choose the right materials for the job, enhancing the performance and longevity of the welding parts in different environments.
Cost-Effectiveness: Welding is generally more cost-effective than alternative joining methods, such as bolting or riveting, especially for larger or bulkier components. The process can be automated in many cases, reducing labor costs and increasing production speed.
Ability to Handle Complex Geometries: In heavy-duty industries, parts are often required to be large and complex in shape. Welding allows for the fabrication of custom designs, with the flexibility to connect components in a wide range of geometries. This is particularly advantageous in industries like shipbuilding, where large hulls and structures need to be welded together precisely.
Enhanced Structural Integrity: Welding parts create a seamless, continuous bond between materials, ensuring maximum strength and minimizing weak points in the finished product. This is essential in high-stress applications like pressure vessels, heavy frames, and structural supports.
Due to these benefits, welding continues to be a critical manufacturing process for the production of large-scale machinery, vehicles, and infrastructure. Its ability to create strong, reliable, and cost-efficient welding parts makes it indispensable in the industrial sector.
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Welding Parts?
Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel Welding Parts
Carbon steel and stainless steel are among the most widely used materials for welding parts due to their strength, availability, and versatility in various industrial applications.
Carbon Steel: Known for its toughness and affordability, carbon steel is commonly used in welding parts for structural applications. It can be welded easily and is suitable for projects like bridges, pipelines, and heavy equipment. Its resistance to corrosion is limited, but it offers a strong, durable weld in many industrial settings.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is prized for its excellent corrosion resistance, especially in environments exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals. Welding parts made from stainless steel are used in industries like food processing, chemical manufacturing, and marine construction. It offers both strength and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Aluminum Welding Parts for Lightweight Structures
Aluminum welding parts are often preferred in industries that require lightweight and high-strength materials, such as the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. Aluminum is known for its low density and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential without compromising structural integrity.
Lightweight and Strong: Aluminum parts are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries due to their ability to reduce the overall weight of the structure while maintaining strength. This makes aluminum welding parts an excellent choice for components like car body frames, aircraft wings, and structural components in buildings.
Good Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, making it resistant to corrosion, which is especially important in outdoor and marine environments.
Specialty Alloys for High-Stress or High-Temperature Applications
For applications that involve high stress or extreme temperatures, such as power plants, gas turbines, and chemical reactors, specialty alloys are often used for welding parts. These alloys are engineered to withstand harsh operating conditions, such as thermal expansion, oxidation, and corrosion, which are typical in high-stress environments.
Nickel Alloys: Nickel-based alloys are often used in high-temperature environments, such as gas turbines and jet engines. These alloys maintain their strength even at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for welding parts exposed to extreme heat.
Titanium Alloys: Titanium is used in industries like aerospace, chemical processing, and medical devices due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion at high temperatures. Welding parts made from titanium alloys are often used in critical applications where durability is essential.
High-Strength Steel Alloys: High-strength steels, such as tool steels and heat-resistant steels, are used for welding parts that need to endure heavy mechanical loads, high temperatures, or both. These materials are commonly found in heavy-duty machinery, cutting tools, and high-performance engines.
Common Materials Used in Welding Parts
The following table summarizes some of the most commonly used materials in welding parts, highlighting their key properties and typical applications:
| Material | Properties | Typical Applications |
| Carbon Steel | Durable, tough, affordable, but susceptible to corrosion. | Structural applications, bridges, pipelines, heavy machinery. |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, strong, high temperature resistance. | Food processing, chemical manufacturing, marine environments. |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good strength-to-weight ratio. | Aerospace, automotive, construction, marine applications. |
| Nickel Alloys | High-temperature resistance, excellent strength at elevated temperatures. | Gas turbines, jet engines, high-temperature industrial applications. |
| Titanium Alloys | Strong, lightweight, highly corrosion-resistant. | Aerospace, medical devices, chemical processing. |
| High-Strength Steel Alloys | High mechanical strength, excellent resistance to wear and heat. | Heavy machinery, cutting tools, high-performance engines. |
A wide variety of materials are used in welding parts depending on the specific requirements of the application. Carbon steel and stainless steel are commonly used for general-purpose applications, while aluminum is favored for lightweight and corrosion-resistant parts. For high-stress or high-temperature environments, specialty alloys such as nickel, titanium, and high-strength steels are often used. The choice of material depends on factors like strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and the specific demands of the application.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体